実際にアプリを作成してみます。
今回は足し算・引き算を行う電卓を簡単に作っていきます。
ちゃんとした電卓を作るのは結構大変なので、ざっくりと作っていきます。
実装
レイアウト
画面を作っていきます。
テーブルの作り方についてはこちらで解説しています。
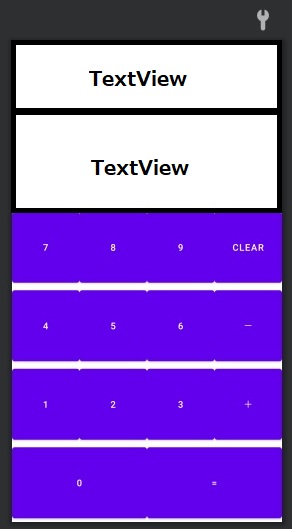
用意するコンポーネント
- TextView×2
計算過程表示、入力値・計算結果表示 - ボタン×14
0~9、CLEAR、+、-、=
デザイン機能で以下のように配置していきます。
<TableLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent">
<TableRow
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textTemp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_span="4" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="2">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textResult"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_span="4" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button7"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="7" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button8"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="8" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button9"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="9" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/buttonClear"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="Clear" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="4" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button5"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="5" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button6"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="6" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/buttonSub"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="-" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="1" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="2" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="3" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/buttonAdd"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="+" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button0"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="0" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/buttonResult"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="=" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
アクティビティ
ロジック
今回は、足し算・引き算のみなので、優先順位を気にせず前方から順に計算していきます。
- 計算式の入力
数字、演算子をリストに格納していく。
→演算子入力時にリストに格納する。 - 演算
以下の計算を演算子の数分繰り返し行う。
①x = 数字[0] + 数字[1] or 数字[0] – 数字[1]
②数字[0] = x
③数字[1]を削除
「1+2+3+4+5」と入力して計算した場合、以下のような流れになります。
| 計算回数 | 計算結果 | リストの値 |
|---|---|---|
| 初期値 | – | 1,2,3,4,5 |
| 1回目 | 1+2=3 | 3,3,4,5 |
| 2回目 | 3+3=6 | 6,4,5 |
| 3回目 | 6+4=10 | 10,5 |
| 4回目 | 10+5 | 15 (計算結果) |
ソースコード
MainActivityファイルに処理を書いていきます。
大きく分けると以下の処理が必要となります。
- アクティビティ開始時の処理
初期処理、イベントリスナの設定 - 数字ボタンを押したときの処理
画面への入力 - 数字以外のボタンを押したときの処理
計算式の作成、計算結果の表示
今回作成したソースでは、Int型の最大値を超える計算を行うと正しい計算が出来ません。
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
companion object {
lateinit var textResult: TextView
lateinit var textTemp: TextView
var clickedNum = mutableListOf<Int>()
var clickedOpe = mutableListOf<Int>()
const val MAX_LENGTH = 9
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
//TextViewコンポーネントの取得
textResult = findViewById(R.id.textResult)
textTemp = findViewById(R.id.textTemp)
//クリックイベントのインスタンス化
val numberButtonClick = NumberButtonClick()
val opeButtonClick = OpeButtonClick()
//ボタンコンポーネントの取得
val button0: Button = findViewById(R.id.button0)
val button1: Button = findViewById(R.id.button1)
val button2: Button = findViewById(R.id.button2)
val button3: Button = findViewById(R.id.button3)
val button4: Button = findViewById(R.id.button4)
val button5: Button = findViewById(R.id.button5)
val button6: Button = findViewById(R.id.button6)
val button7: Button = findViewById(R.id.button7)
val button8: Button = findViewById(R.id.button8)
val button9: Button = findViewById(R.id.button9)
val buttonClear: Button = findViewById(R.id.buttonClear)
val buttonAdd: Button = findViewById(R.id.buttonAdd)
val buttonSub: Button = findViewById(R.id.buttonSub)
val buttonResult: Button = findViewById(R.id.buttonResult)
//各ボタンにクリックリスナを設定
button0.setOnClickListener(numberButtonClick)
button1.setOnClickListener(numberButtonClick)
button2.setOnClickListener(numberButtonClick)
button3.setOnClickListener(numberButtonClick)
button4.setOnClickListener(numberButtonClick)
button5.setOnClickListener(numberButtonClick)
button6.setOnClickListener(numberButtonClick)
button7.setOnClickListener(numberButtonClick)
button8.setOnClickListener(numberButtonClick)
button9.setOnClickListener(numberButtonClick)
buttonClear.setOnClickListener(opeButtonClick)
buttonAdd.setOnClickListener(opeButtonClick)
buttonSub.setOnClickListener(opeButtonClick)
buttonResult.setOnClickListener(opeButtonClick)
}
class NumberButtonClick() : View.OnClickListener {
override fun onClick(v: View?) {
if (v != null) {
//クリックされたボタンを取得
val button: Button = v.findViewById(v.id)
//最大文字数を越えていない場合のみ入力を受け付ける
if(textResult.text.length < MAX_LENGTH) {
if (Integer.parseInt(button.text.toString()) <= 9) {
if (textResult.text.isEmpty()) {
textResult.text = button.text
} else {
if (textResult.text.equals("0")) {
//0始まりの場合は連続で入力させない
textResult.text = button.text
} else {
//それ以外は入力値を末尾に追加する
var tempStr = textResult.text.toString() + button.text
textResult.text = tempStr
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
class OpeButtonClick() : View.OnClickListener {
override fun onClick(v: View?) {
if (v != null) {
if(textResult.text.isNotEmpty()) {
//クリックされたボタンを取得
val button: Button = v.findViewById(v.id)
when (v.id) {
R.id.buttonAdd -> {
addTempText(button)
}
R.id.buttonSub -> {
addTempText(button)
}
R.id.buttonClear -> {
allClear()
}
R.id.buttonResult -> {
calcResult()
}
else -> {
}
}
}
}
}
private fun addTempText(button: Button) {
clickedNum.add(Integer.parseInt(textResult.text.toString()))
clickedOpe.add(button.id)
var tempStr = textTemp.text.toString() +
textResult.text.toString() +
button.text.toString()
textTemp.text = tempStr
textResult.text = ""
}
private fun allClear() {
textTemp.text = ""
textResult.text = ""
clickedNum.clear()
clickedOpe.clear()
}
private fun calcResult() {
clickedNum.add(Integer.parseInt(textResult.text.toString()))
//入力値を前方から順に計算する
clickedOpe.forEach { buttonId ->
if(clickedNum.size > 1) {
val number1 = clickedNum[0]
val number2 = clickedNum[1]
when (buttonId) {
//計算結果を格納し直す
R.id.buttonAdd -> {
clickedNum[0] = number1 + number2
}
R.id.buttonSub -> {
clickedNum[0] = number1 - number2
}
}
}
//計算が終わった値を削除する
clickedNum.removeAt(1)
}
//入力を初期化して計算結果を表示する
textResult.text = clickedNum[0].toString()
textTemp.text = ""
clickedNum.clear()
clickedOpe.clear()
}
}
}
まとめ
足し算・引き算のみを行う簡易な電卓を作成しました。
まずは、Android Studioや言語に慣れるために、書いてみると手っ取り早く覚えられます。
しっかり身につくまでは、こだわり過ぎず実践していくと良いでしょう。
実機にインストールする方法も紹介しています。